Paraplegia refers to an impairment that causes a person’s leg to move in a way that is abnormal. Paralysis is often associated with paraplegia, but it can also occur without a spinal injury. Paralysis caused by paralysis or motor control disorders can still cause pain and loss of movement, but it is not the same as paraplegia.
Paraplegia is caused by an injury to the spinal cord. The spinal cord is located inside the spinal canal and is located just outside the skull. It transfers information from the brain to the rest of the body through nerves. When nerve cell damage occurs, the nerve line is damaged and usually can never be repaired. The resulting paralysis is usually temporary and does not result in loss of function.
Paraplegia can occur due to spinal cord injury. Spinal trauma, spinal stenosis, tumors, and meningitis can damage the spinal cord. Sometimes a pinched or pinched spinal nerve causes paralysis or weakness in that area.
Other symptoms associated with paraplegia include weakness, muscle cramps, difficulty swallowing, and inability to walk. A child with lower limb paralysis can easily go unnoticed and may not have clear signs that he or she needs help.
Paraplegia can be a serious medical condition that can be difficult to diagnose. Since there is no definitive test for paraplegia, doctors can use a variety of tests to determine if a patient is suffering from it. In some cases, an examination of the child’s movements may be sufficient to make a diagnosis. In other cases, a medical examination may be required to rule out a more serious condition such as encephalitis or meningitis.
Paralysis can occur in one or both of the spinal nerves that transmit information to the limbs. The most common form of paralysis is called brachiospinal neuralgia. It refers to the abnormal excitation of nerve fibers in the brain. This can lead to weakness or loss of muscle function in the affected area. Spinal stenosis, another form of paralysis, results in abnormal movement of the vertebrae, resulting in weakness and stiffness of the spine.
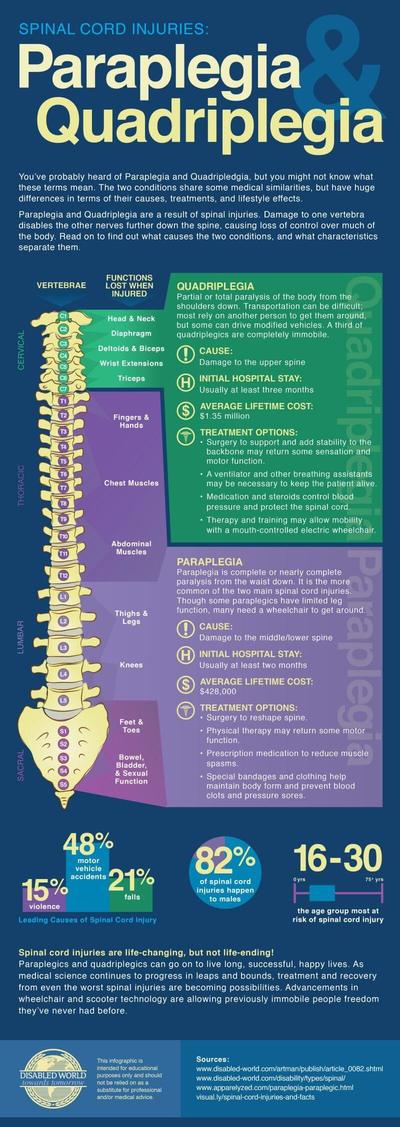
Sometimes the spine becomes damaged from infection or trauma, and infection can result in nerve compression. This type of paralysis is referred to as myoneural neuropathy. Muscle spasms are another form of paralysis that results in abnormal firing of muscles in the upper extremities. Muscle contractions can cause weakness in the legs, or loss of muscle strength.
Para paraplegia can be caused by many factors, so the treatment options are different for each individual case. Some of the treatment options can include physical therapy, physiotherapy, and sometimes surgery. Surgery may be needed to replace the nerves.
Physiotherapists help patients with their mobility problems through physical therapy and exercises. Patients usually get some form of physical activity to help increase flexibility, coordination, and strength.
Physical therapists help patients with their physical therapy through various exercises and stretches. These exercises include activities like walking, swimming, and stair climbing stairs. They also use soft equipment to help patients get up and down from stairs. Patients also get exercise to reduce or eliminate muscle spasms caused by muscle contractions or spasms.
In some cases, surgeons may perform surgery to help patients with spinal cord traction. This surgery involves implanting a titanium rod into the spinal cord through an incision. This rod can help in the manipulation of the spinal cord and help with the movement of the spine and the lower back. In severe cases, doctors may need to perform spinal decompression to increase the movement and stability of the spine and increase the amount of movement.
Paraplegia can cause problems with swallowing and breathing and can also cause swallowing problems. A patient may be able to breathe with the use of a ventilator to provide air to the lungs. Some people will not be able to swallow properly on their own, and this may require a feeding tube. Breathing devices are also used. Patients may be unable to move their mouths and noses.