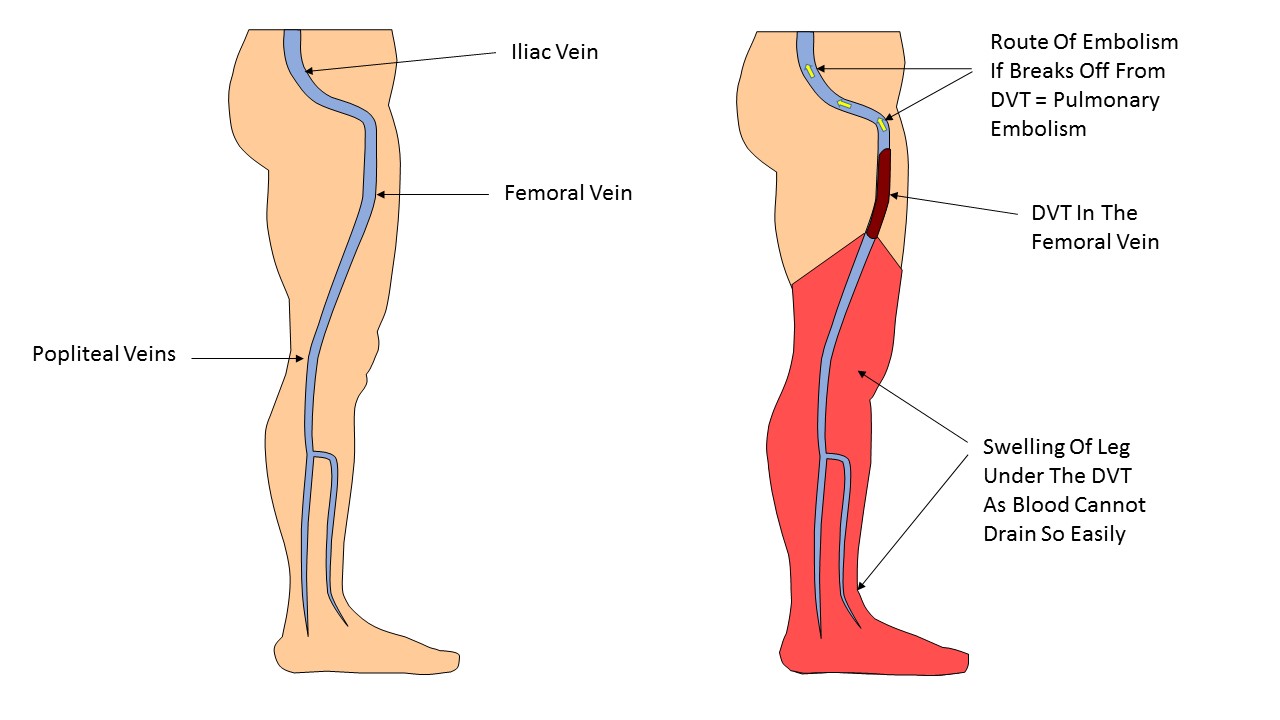
Deep vein thrombosis is a blood clot in the leg. Occurs when blood accumulates in the veins. It can develop when you have any number of medical conditions that interfere with blood flow. It can also happen when you are bedridden, after surgery, or due to poor nutrition.
These conditions can make it difficult for the veins to drain from the veins caused by thrombosis and cause them to crack. These cracks allow blood to accumulate and can grow in size and cause a clot to form, which is then flushed out in the urine. This clot may be large enough to block blood flow to the leg. There is also some evidence that the clot can break up into tiny fragments and travel to another part of the body.
As mentioned, vein thrombosis is usually not serious. However, if a clot forms, it can cause problems and may require surgery or blood transfusion if there is a risk of it growing into a larger one.
If the blood clot is large enough, it can travel through the blood vessels and settle in the lungs. The clot can start to build up and become very large. If this happens, it will block the airways.
Although most deep vein thrombosis is not fatal, it can sometimes cause serious complications. In many cases, they can cause pulmonary embolism, in which a clot blocks the airways. This can be life threatening and usually requires immediate surgery. It is also possible that the clot breaks down and travels through the blood vessels.
- If the clot is detected early enough, it usually does not lead to serious complications. However, if left for too long or left untreated, the chances of permanent damage increase dramatically. Many people with deep vein thrombosis are at risk of stroke, heart attack, and other serious complications.
- If you notice that a blood clot has entered your lungs and feel dizzy or nauseous, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible. This is because it is a sign that your clot may be blocking your airways.
Once you know about the problem, you can start treating it to remove the blood clot. It is important to remember to keep your feet high and always keep your shoes away from your feet to prevent blood clotting. Applying a cuff to your leg will also help maintain blood flow, preventing further congestion.
Your doctor may recommend medication, surgery, or a combination of both to remove the blood clot. He or she may also recommend a procedure known as arteriotomy, which is a procedure in which your artery or vein is cut and the clot is removed. In addition to this, he or she may refer you to a vein specialist for a treatment known as mentoplasty, which involves removing part or all of a vein to prevent a clot from forming.
Some of the drugs used to treat vein thrombosis include nifedipine, atabrine, amlodipine, vincristine, and stavudine. Another option is surgery. A procedure called venography is used to monitor the blood clot and its progress and to determine the best course of action for a particular patient.
Because of the complexity of the procedure, many people choose to wait until they have symptoms for a while before undergoing the procedure. If you are suffering from a symptom and are waiting for surgery, it could mean that the clot will go into remission or that it will go away on its own over time. Your doctor may decide to use other medicines to treat your symptoms, and you may be advised to undergo surgery only if the problem gets worse. If you have a history of venous thrombosis, your doctor can also monitor the situation.
If you are suffering from venous thrombosis, it is best to discuss the risks with your doctor before proceeding with surgery. Your doctor will be able to recommend surgery and a treatment plan that will give you the best results. In many cases, venous thrombosis is caused by a family history of the condition. if you smoke, it can also affect your choice of surgery.
In some cases, venous thrombosis can be treated with surgery, even if you have no symptoms. In this case, your doctor will likely prescribe medication to help remove the clot. You may then be advised to refrain from intercourse to prevent the clot from reoccurring. In some cases, a vein specialist may perform a procedure known as sclerotherapy, which is done to clear a blockage in a vein and prevent scarring.