
A manic episode is defined as a prolonged period of abnormally high or irritable emotion, rapid racing thoughts, jittery movements, irritability, insomnia, and many other extreme and unusual behaviors. People who have manic episodes are commonly described as hyperactive, irritable, extremely talkative, easily agitated, irritable, depressed, irritable, and have problems concentrating. People may also experience hallucinations, delusions, and psychotic episodes, which mean a break from reality.
People with bipolar disorder may also exhibit symptoms similar to those of schizophrenia. They may display paranoid thoughts and fear, as well as having hallucinations. Some of the most common hallucinations are delusions, hallucinations, or delusions that do not resemble anything they are hearing or seeing. They include auditory hallucinations (hallucinations), visual hallucinations (seeing things they are not), delusions of persecution, and delusions of grandeur.
People with manic episodes often experience psychotic episodes such as hallucinations, delusions, or psychosis. The symptoms of psychosis are similar to those of schizophrenia, but are usually much worse. People with this disorder suffer from hallucinations, megalomania, or psychosis and experience bizarre illusions that can lead to physical attacks.
Manic episodes can last for weeks or months. They usually affect the social and professional life of a person and cause serious disruptions in his daily life.
The cause of bipolar disorder is unknown. It is thought to happen when a chemical imbalance in the brain causes a change in a person's way of thinking. This change in thinking occurs in response to various situations that a person faces, but the exact reasons for this are not known. Most experts believe that manic episodes have a biological basis.
Certain medications can cause a manic episode, such as antidepressants, stimulants, and many anxiety medications. However, it is believed that certain chemicals in the body can also trigger a seizure. This includes dietary substances, medications, and stress. Some of these chemicals cause the body to release certain hormones, which can trigger the release of certain chemicals, which can trigger a manic episode.
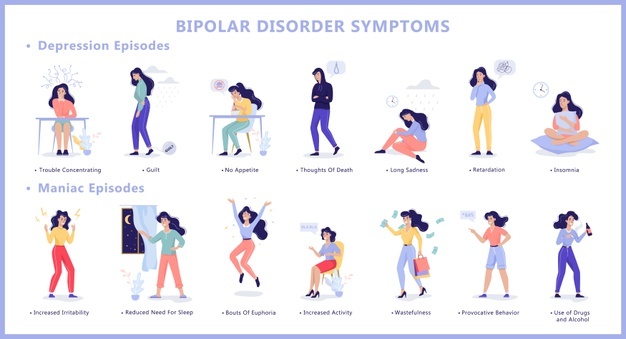
There are also certain symptoms that can occur during a manic episode
These symptoms include: excessive talkativeness, increased energy levels, extreme optimism, a sense of guilt, irritability, increased activity, talking about death or suicide, racing thoughts and racing emotions, insomnia, being unable to sleep, rapid heart rate, extreme joy and happiness, feeling as if you can't control your body, becoming addicted to drugs and alcohol, or being easily agitated. Some of these symptoms may last only for a short time, or last for days, months, while others may last for weeks.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek treatment for yourself and get help. It is also important to learn how to identify and treat the symptoms so that you can manage and control your episodes.
Symptoms of a manic episode include: elevated moods, rapid speech, increased energy, racing thoughts, increased need for sleep, and euphoria. If you suspect that you are experiencing some of the symptoms of a manic episode, see your doctor for a medical evaluation. A psychiatrist or psychologist can help you determine if you are having an episode and what steps to take to help you with your disorder.
Bipolar disorder can be treated in a number of different ways. One of the most common ways to manage the disorder is to use antidepressants. Many medications can help you control the symptoms of the condition. However, it is important to remember that medication alone is not a cure.
Medication is used primarily as a means to prevent recurrences of the episode rather than actually cure the disorder. Sometimes, medication is used for some people. It can be very hard to live with this condition because medication can cause side effects, which can include mood swings. Some people have had success with using anti-depressants, which can cause a reduction of the use of prescription medication.
The best treatment is a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. When used together, therapy and medication can help to improve both the physical and emotional symptoms associated with bipolar disorder.